E-WASTE
In the talk around climate change, a new light is emerging, e -waste management. Electronic waste, or e-waste, consists of devices powered by electricity, solar, or batteries that have reached the end of their life cycle. These gadgets often end up misplaced in our reducing, reusing, and recycling efforts. However, ignorance is not bliss when it comes to managing e-waste until we explore how we can identify electronic waste, understand e-waste management process, and contribute to a cleaner, greener planet.
Electronic waste includes any device powered by electricity, solar energy, or batteries that is no longer useful or functional, encompassing a wide variety of items, from old cell phones, laptops, and televisions to kitchen appliances, cables, and batteries. With technology advancing rapidly, the lifespan of these devices is shortening, leading to an increase in e-waste. Recognizing e-waste is the first step in addressing the issue. E-waste contains hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can harm the environment and human health if not disposed of properly.
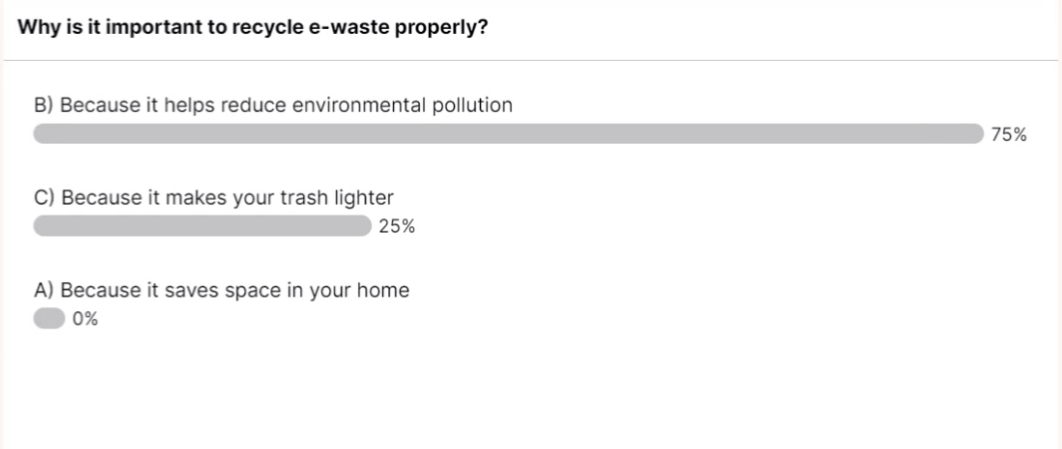
Moreover, these devices often contain valuable materials such as gold, silver, and copper, which can be recycled and reused. Proper e-waste management not only mitigates environmental risks but also conserves resources, reduces the need for raw material extraction, and supports a circular economy. E-waste management is a comprehensive process that ensures discarded electronics are handled in an environmentally friendly and resource-efficient manner
The journey of e-waste management begins with the collection of discarded electronic items. Special bins and collection centers are set up to gather these items from households, businesses, and public spaces. Recording and categorizing this data helps track the amount and type of waste being processed, providing insights into the effectiveness of e-waste management programs aimed at reducing, reusing and recycling.
E-waste is then dismantled and disassembled to separate valuable components allowing for the extraction of precious metals and other useful materials such as circuit boards, batteries, plastics that are separated for further processing creatively repurposing e-waste into new and innovative items, giving old electronics a second life and reducing the overall waste footprint and disposing the hazardous materials in an environmentally safe manner.